If your vehicle’s check engine light has turned on, and you’re seeing the P2104 code pop up, it can trigger a wave of concern. This particular code indicates an issue with the Throttle Actuator Control System that forces your car into idle mode.
In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about the P2104 code—its symptoms, causes, diagnostic procedures, and how to fix it effectively.
Key Takeaway
The P2104 code signals a serious issue with your vehicle’s throttle actuator control system. When this code appears, it typically indicates that the engine has defaulted to a forced idle mode for safety reasons.
Ignoring this warning can lead to further complications. It’s crucial to address the underlying problem promptly to maintain optimal vehicle performance and ensure your safety on the road.
This code doesn’t just affect how smoothly your car runs; it may also impact fuel efficiency and accelerate wear on other engine components. Proper diagnosis is essential for effective repairs.
Stay vigilant! If you encounter symptoms associated with the P2104 code, taking action quickly will save time and money in the long run.
What does the P2104 code mean?
The P2104 code indicates a problem with the throttle actuator control system. Specifically, it points to a forced idle condition in your vehicle.
This code is triggered when the Engine Control Module (ECM) detects an abnormal scenario within the throttle body or its related components. In essence, it’s telling you that something isn’t functioning as intended.
When this happens, your car’s computer may limit engine power to prevent further issues. This can result in reduced acceleration and overall performance.
Understanding this code is crucial for diagnosing potential problems before they escalate into more significant repairs. Addressing the P2104 promptly ensures your vehicle runs smoothly and safely on the road.
What are the common symptoms of a P2104 code?
When your vehicle throws a P2104 code, it often reveals itself through several noticeable symptoms. One of the first signs is an unusual drop in engine performance. You might experience sluggish acceleration or difficulty reaching higher speeds.
Another common symptom is the illumination of the check engine light on your dashboard. This warning signals that something isn’t quite right under the hood and should not be ignored.
Drivers may also notice erratic idling. The engine could rev up or down unexpectedly, creating a frustrating driving experience.
In some cases, you may encounter limited throttle response. Even pressing down hard on the accelerator can result in minimal power output from your vehicle, making it feel like you’re dragging anchor.
If any of these symptoms arise alongside a P2104 code reading, it’s time to investigate further and address potential issues promptly.
What causes a P2104 code?
The P2104 code often arises due to issues within the throttle actuator control system. This could stem from a faulty throttle body or miscommunication between sensors.
Electrical problems are another common culprit. Damaged wiring, corroded connectors, or short circuits can disrupt signals sent to the engine control unit (ECU).
A malfunctioning accelerator pedal position sensor may also trigger this code. If the sensor fails to relay accurate data, it compromises engine performance.
Vacuum leaks can add complexity as well. They affect air intake readings and create inconsistencies in how the vehicle responds when accelerating.
Low battery voltage presents an unexpected challenge too. Insufficient power can lead to erratic behavior in various electronic systems connected to your vehicle’s engine management system.
How is a P2104 code diagnosed?
Diagnosing a P2104 code begins with scanning the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system. A professional or a DIY enthusiast typically uses an OBD-II scanner to retrieve the trouble codes stored in the engine control unit (ECU).
Once the P2104 code is identified, it’s crucial to inspect related components such as wiring, connectors, and fuses for any visible damage. This step helps rule out simple issues that could cause erratic signals.
Next, technicians often perform tests on the throttle actuator itself. They check for proper operation and response when commanded by the ECU.
Monitoring live data can also provide insights into how various sensors interact during different driving conditions. This information assists in pinpointing faults more accurately.
Conducting a visual inspection of vacuum lines and other potential leaks ensures all aspects are covered before moving forward with repairs.
How do I fix a P2104 – Throttle Actuator Control System – Forced Idle ?
Fixing a P2104 code involves several steps to ensure your throttle actuator control system functions properly again.
Start by inspecting the wiring and connectors associated with the throttle body. Look for any signs of damage, corrosion, or loose connections. Repair or replace as needed.
Next, check the throttle body itself. Clean it thoroughly to remove carbon buildup that can impede its movement. A clean surface allows better airflow and enhances responsiveness.
If everything looks good but you still have issues, test the throttle position sensor (TPS). Ensure it’s functioning correctly; if not, replacement will be necessary.
Sometimes software updates may resolve communication errors between components. Consult your vehicle’s manufacturer for any available updates that might address this issue.
Consider using an OBD-II scanner after repairs to reset any stored codes and verify that the problem is resolved before hitting the road again.
How much does it cost to fix a P2104 code?
The cost to fix a P2104 code can vary significantly depending on several factors. Typically, you might expect to pay anywhere from $100 to over $1500 for repairs :
- Throttle body cleaning: $75-150
- Throttle body replacement: $300-600
- APP sensor replacement: $100-300
- PCM replacement: $500-1500
Are there any other codes that may be related to a P2104 code?
When dealing with the P2104 code, it’s essential to be aware of other related trouble codes that might appear :
- P2110 – TAC system forced limited power
- P2105 – TAC system forced engine shutdown
- P2106 – TAC system forced limited RPM
- P2135 – APP sensor circuit malfunction
- P0121 – APP sensor range/performance
Frequently Asked Questions About P2104 Code :
Can I still drive with a P2104 code?
Driving with a P2104 code is generally not recommended. The throttle remains restricted to idle, making it extremely challenging to control the vehicle, particularly on highways. It’s important to diagnose and resolve the root problem promptly.
Can a bad throttle position sensor cause a P2104?

A bad throttle position sensor (TPS) can indeed trigger a P2104 code. This component plays a crucial role in communicating the position of the throttle plate to the engine control module (ECM). If it malfunctions, the ECM may receive incorrect information about how open or closed the throttle is.
When this happens, you might experience erratic acceleration or stalling. The vehicle could enter a forced idle state as a safety measure to prevent further damage.
It’s essential to diagnose any issues with the TPS early on. Ignoring signs like poor fuel efficiency and unexpected RPM changes can lead to more significant problems down the line. A simple replacement of this sensor often resolves related codes, including P2104, restoring normal function and performance to your vehicle.
Can a vacuum leak cause a P2104 code?

A vacuum leak can indeed trigger a P2104 code. When there’s an unintended gap in the intake system, excess air enters, disrupting the air-fuel mixture. This imbalance creates issues for the throttle actuator control.
The engine management system struggles to maintain optimal performance. It may interpret this as a malfunction in the throttle control system itself. As a result, it activates limp mode or forced idle to protect your vehicle from potential damage.
Identifying a vacuum leak isn’t always straightforward. You might notice symptoms like rough idling or stalling engines while driving. Sometimes you’ll hear hissing sounds coming from under the hood.
If you’re experiencing these signs alongside a P2104 code, it’s wise to inspect for leaks promptly. Addressing any found issues can restore normal function and improve overall drivability.
Can low battery voltage cause a P2104?
Low battery voltage can indeed trigger a P2104 code. This happens because the throttle actuator relies on sufficient power to function correctly.
When the battery voltage drops below the required level, it may hinder communication between various components in the throttle control system. The Electronic Control Module (ECM) detects this inconsistency and raises red flags through trouble codes like P2104.
Additionally, when low voltage is present, other electrical systems might also malfunction. This cascade effect can lead to further complications with vehicle performance.
If your car struggles to start or exhibits erratic behavior alongside a P2104 code, checking your battery and charging system should be one of your first steps. Ensuring that you have robust battery health can prevent unnecessary stress on critical engine management components.
Can a bad accelerator pedal cause a P2104?
A malfunctioning accelerator pedal can indeed trigger a P2104 code. The throttle actuator control system relies on signals from the accelerator pedal position sensor to regulate engine power.
When the accelerator pedal is damaged or faulty, it may send incorrect readings to the engine control unit (ECU). This miscommunication can lead to unintended changes in throttle response or even forced idle conditions.
Drivers may notice unusual acceleration behavior, such as delayed responses or sudden drops in power. These symptoms are often linked directly back to issues with the accelerator pedal assembly.
If you suspect that the problem lies within this component, it’s essential to have it inspected thoroughly. A simple calibration might resolve minor glitches, but more significant damage could require replacement for optimal performance.
Can a clogged catalytic converter cause P2104?
A clogged catalytic converter can indeed lead to a P2104 code. When the exhaust flow is restricted, it creates back pressure in the engine. This situation disrupts normal operation and may trigger the throttle actuator control system into forced idle mode.
The vehicle’s computer tries to protect the engine from damage by limiting power output. If you notice sluggish acceleration or stalling, it might be time to check the catalytic converter.
Symptoms of a failing converter include unusual noises or foul smells from under your vehicle. Ignoring these signs can result in more severe issues down the line.
Regular maintenance helps prevent such clogs. Replacing old spark plugs and ensuring fuel quality can go a long way in keeping your exhaust system clear and functional.
Can a bad mass airflow sensor cause a P2104 code?
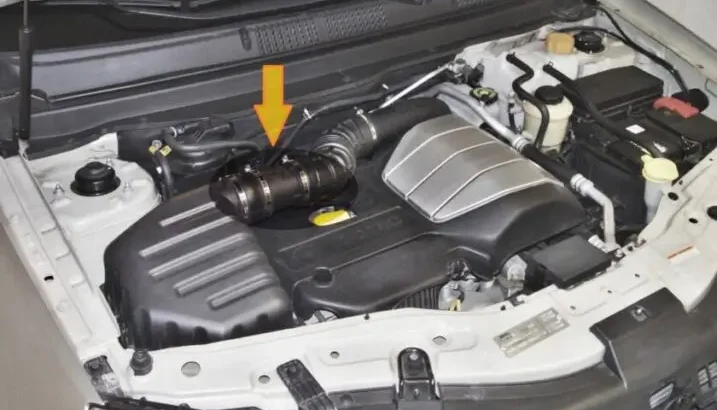

A malfunctioning mass airflow (MAF) sensor can indeed contribute to a P2104 code. The MAF sensor measures the amount of air entering your engine, which is crucial for optimal fuel-air mixture. If it fails or provides incorrect readings, the engine control unit may struggle to adjust throttle position accordingly.
When the ECU detects discrepancies in airflow data, it can trigger safety protocols. These protocols often include activating forced idle mode as a protective measure against potential damage.
If your vehicle exhibits symptoms like erratic idling or poor acceleration alongside a P2104 code, checking the MAF sensor should be high on your troubleshooting list. Cleaning or replacing this component might resolve both issues effectively without requiring extensive repairs elsewhere in the system.
What is the difference between P2104 and P2135?
When discussing the P2104 code, it’s essential to differentiate it from other similar codes, particularly P2135. While both codes are associated with throttle control issues, they stem from different problems within the system.
The P2104 code pertains specifically to the “Throttle Actuator Control System – Forced Idle.” This indicates that your vehicle’s throttle actuator is being forced into an idle state due to detected faults or malfunctions in its operation.
On the other hand, the P2135 code relates more closely to a malfunctioning accelerator pedal position sensor circuit. It signals that there’s a discrepancy between two sensors that monitor accelerator pedal position. If these sensors don’t match up correctly, it can lead to inconsistent throttle response and potential safety concerns for driving.
In essence, while both codes point towards issues in throttle control systems, their origins and specific implications differ significantly. Understanding this distinction can help you diagnose your vehicle’s issue more accurately and apply appropriate fixes efficiently. Keeping an eye on your dashboard lights and understanding what these codes mean can save you time and money down the road.
